Cooling system and types of cooling system in power plant
- Mech Surge

- Apr 25, 2021
- 2 min read
During combustion method the peak gas temperature within the cylinder of an internal combustion engine is of the order of 2500 K.
Maximum metal temperature for the inside of the combustion chamber space are limited to much lower values than the gas temperature by a large number of considerations and thus cooling for the cylinder head, cylinder and piston must therefore be provided. Necessity of engine cooling arises due to the following fact.
Types of cooling system
Cooling system is classified into two types. They are
Air or direct cooling system
Liquid or indirect cooling system
Open cooling system
Natural circulation (thermo system)
Forced circulation system
Evaporation cooling system
Open cooling system :
This system is applicable only wherever plenty of water is available. The water from the vessel is directly supplied through an inlet valve to the engine cooling water jacket.
The hot water coming out of the engine isn’t cooled for reuse however it’s discharged.
Natural circulation system :
The system is closed one and designed so that the water could flows into naturally because of the difference in density of water at different temperatures.
It consists of water jacket, radiator and a fan. Once the water is heated, its density decreases and it tends to rise, whereas the colder molecules tend to sink.
Circulation of water then is obtained because the water heated within the water jacket tends to rise and also the water cooled within the radiator with the help of air passing over the radiator either by ram effect or by fan or jointly tends to sink.
Arrows show the direction of natural circulation which is slow.
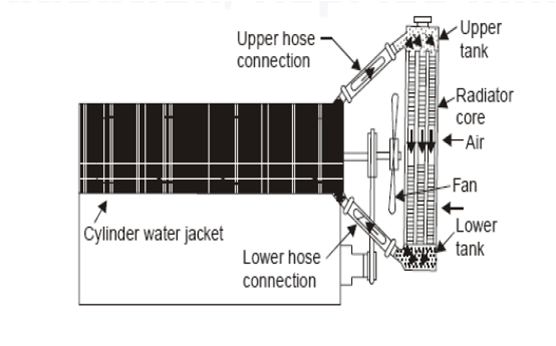
Forced circulation system :
The system consists of pump, water jacket in the cylinder, radiator, fan and a thermostat.
The coolant is circulated through the cylinder jacket with the help of a pump, which is usually a centrifugal type and driven by the engine.
The function of thermostat that is fitted within the upper hose connection initially, prevents the circulation of water below a certain temperature (usually upto 85°C) through the radiation so that water gets heated up quickly.



Comments